| CAS No. | 23783-26-8 | EINECS No. | 405-710-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5O6P | Molecular Weight | 156 |
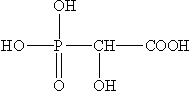
HPAA is a powerful and well-known ferrous metal corrosion inhibitor for all-organic cooling water formulations. Because HPAA can improve zinc solubility. So HPAA can be used either on its own or as part of an all organic or low level zinc program. HPAA gives significantly better performance than commodity phosphonates such as HEDP. Its corrosion inhibition ability is 5-8 times better than other of HEDP and EDTMP. When built with low molecular polymers, its corrosion inhibition effect is even better. Moreover, HPAA is also a cost effective alternate to sodium molybdate. It can be more easily tested in the field.With HPAA, you can restore the profitability of water treatment programs by increasing formulation profitability. HPAA is a environmentally friendly products. HPAA provides higher biodegradability (93%) and much better environmental profile versus other available programs.
| Parameter | Standard |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Dark umber liquid |
| Active content, % | 50.0 min |
| Total phosphonic acid (as PO43-), % | 25.0 min |
| Phosphoric acid (as PO43-), % | 1.50 max |
| Density (20℃), g/cm3 | 1.30 min |
| pH (1% water solution) | 1.0-3.0 |
HPAA is mainly used as cathode corrosion inhibitor in well-controlled halogenated cooling system such as steel & iron, petrochemcal, power plant and medical industries. When built with zinc salt, the effect is even better.
| HPAA Liquid | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25L Drum | 200L Drum | 1000L IBC | ISO Tank | ||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Storage for 10 months in shady room and dry place. | |||||
| Hazard Information | Safety Precaution |
|---|---|
|
|
|
| Once contacted with eye and skin, flush with plenty of clean water. | |